Back in the 1990s, the EPA introduced rules to stop acid rain by cutting the emission of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide. Critics thought it couldn’t be done, but inventive engineers came up with new and better ways to scrub the pollutants out of the smokestacks.
Now the same is believed for the newly proposed EPA regulations on carbon emissions, but there are many reasons to disagree with the skeptics. Many opposed are saying that the new regulations will bring elevated electricity bills and even plunge the nation into blackouts. But, in reality, emissions cuts have already been achieved in some states and those states are faring better economically than many other parts of the United States.
The new EPA carbon rules in a nutshell:
 By 2030 the EPA seeks to reduce America’s carbon dioxide emissions 30% from 2005 levels.
By 2030 the EPA seeks to reduce America’s carbon dioxide emissions 30% from 2005 levels.- States will have until June 30, 2016 (with the potential for some extensions) to come up with a plan on how to implement the rule and reduce their average emissions per megawatt-hour of electricity. If they refuse the EPA says it will impose its own plan.
Success Stories:
One way that some states have got a foot up on meeting the emissions standards is by joining the Northeastern cap-and-trade program known as the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative, which first put in a carbon cap in 2009. In the cap-and-trade system, the participating state governments placed an upper limit on total carbon emissions and issued permits for those emissions, which companies bought and sold from one another.
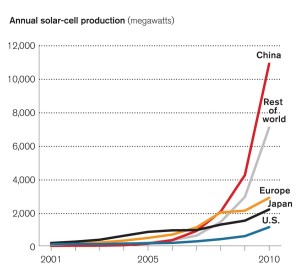
Nine northeastern states have already entered the program and have substantially reduced their carbon emissions in recent years. At the same time, those states have had stronger economic growth than the rest of the country.
Since 2009, the nine states have cut their emissions by 18 percent, while their economies grew by 9.2 percent. By comparison, emissions in the other 41 states fell by 4 percent, while their economies grew by 8.8 percent.
The states in the program reduced emissions faster and more efficiently than was previously assumed, and this gives a ray of hope to the rest of the United States. The sharp cut in emissions in the Northeast did not inhibit the economy there from doing just as well as elsewhere.
What’s the Problem, then?
 Some of the biggest opposition to the new regulations comes from heavily coal dependent states. However, many of them have been given more moderate goals to meet with the new regulations due to their reliance on coal and their limited renewable energy resources. But even in states that have made big cuts, the Obama plan is inciting some wariness with officials in those regions, who are pointing out that the plan would burden them with rigorous targets requiring them to go further in reducing emissions.
Some of the biggest opposition to the new regulations comes from heavily coal dependent states. However, many of them have been given more moderate goals to meet with the new regulations due to their reliance on coal and their limited renewable energy resources. But even in states that have made big cuts, the Obama plan is inciting some wariness with officials in those regions, who are pointing out that the plan would burden them with rigorous targets requiring them to go further in reducing emissions.
There are many different options that states can choose between when determining how to cut carbon emissions though. While cutting emissions in general is the goal, the ways of achieving those cuts can either push progress forward even more or just do what little needs to be done in order to meet the requirements. By choosing to rely on energy storage and renewable energy sources states will be able to not only cut emissions but help the world to move forward in a more sustainable way, with economic benefits for those states.
Why is Energy Storage a good option?
Energy storage has the potential to not only cut costs, but also allow us to keep energy in reserves for the future and times of emergency. Energy Storage systems are also fuel neutral, which means regardless of how the energy was generated the storage systems can save it.
Energy storage cuts costs primarily by lowering the overall cost of electricity. It also allows customers to avoid premium pricing when demand for electricity is highest. But most importantly, energy storage helps to reduce the amount of power outages and equipment failures that take place as well as limiting the amount of time the power is out. This not only helps to save time and money but it also can help to save lives.
Why are renewables a good option?
 Renewable resources are inexhaustible. They can be utilized without any fear of depletion. Unlike the burning of fossil fuels, which spew dangerous greenhouse gases that lead to global warming, wind and solar farms are emissions free. That is just one of the many reasons to convert to renewables. By switching there is also a great increase in job creation. In total there were 142,698 solar workers in the U.S. as of November 2013. This is a 20 percent increase over 2012 figures and ten times higher than the national average employment growth rate, which was 1.9 percent. Veterans also make up about 9 percent of the solar workforce compared with 7.5 percent of the national economy. These numbers are all very optimistic, but while the U.S. could see million of new jobs in renewable energy and energy efficiency, this will only happen with the necessary leadership, research, development, and public policy at the federal and state levels. The new EPA regulations took that first step.
Renewable resources are inexhaustible. They can be utilized without any fear of depletion. Unlike the burning of fossil fuels, which spew dangerous greenhouse gases that lead to global warming, wind and solar farms are emissions free. That is just one of the many reasons to convert to renewables. By switching there is also a great increase in job creation. In total there were 142,698 solar workers in the U.S. as of November 2013. This is a 20 percent increase over 2012 figures and ten times higher than the national average employment growth rate, which was 1.9 percent. Veterans also make up about 9 percent of the solar workforce compared with 7.5 percent of the national economy. These numbers are all very optimistic, but while the U.S. could see million of new jobs in renewable energy and energy efficiency, this will only happen with the necessary leadership, research, development, and public policy at the federal and state levels. The new EPA regulations took that first step.
The potential ways of meeting the new EPA emissions regulations are in abundance, but the only way we will start seeing change is if we begin to implement those solutions. By turning to renewable energy sources and supporting energy storage we can make sure that our country is not only able to meet the EPA regulations but goes above and beyond and to help clean up and protect our earth to make it safe for our children and their future. It is already evident that states can cut emissions and still see economic growth, so what are we waiting for?
















 By 2030 the EPA seeks to reduce America’s carbon dioxide emissions 30% from 2005 levels.
By 2030 the EPA seeks to reduce America’s carbon dioxide emissions 30% from 2005 levels.